Vector Annotation
Updated at January 22nd, 2025
Vector annotation is a method used to label and annotate specific points, lines, or regions in an image using geometric shapes. This approach is widely applied in fields like mapping, computer vision, and data visualization to create structured datasets for machine learning or other analytical tasks.
What Is Vector Annotation?
Vector annotation involves marking elements within an image using vector shapes such as points, lines, arrows, or polygons. These annotations capture the spatial relationships and geometric properties of the elements being labeled. Unlike raster annotation, which focuses on pixel-level categorization, vector annotation operates at a higher level of abstraction by defining areas or objects with precise coordinates and shapes.
Tools for Vector Annotation
To perform vector annotation effectively, we use several tools:

- Point: Marks specific locations within an image.
- Line: Connects two or more points to represent linear features.
- Arrow: Indicates direction or flow, often used in diagrams and mappings.
- Rectangle: Defines rectangular regions to annotate bounded areas.
- Polygon: Encloses irregular shapes with a series of connected points.
- Cuboid: Represents 3D objects by annotating their projections in 2D.
- Slider Rectangle: A dynamic rectangular tool that adjusts dimensions interactively for precise annotations.
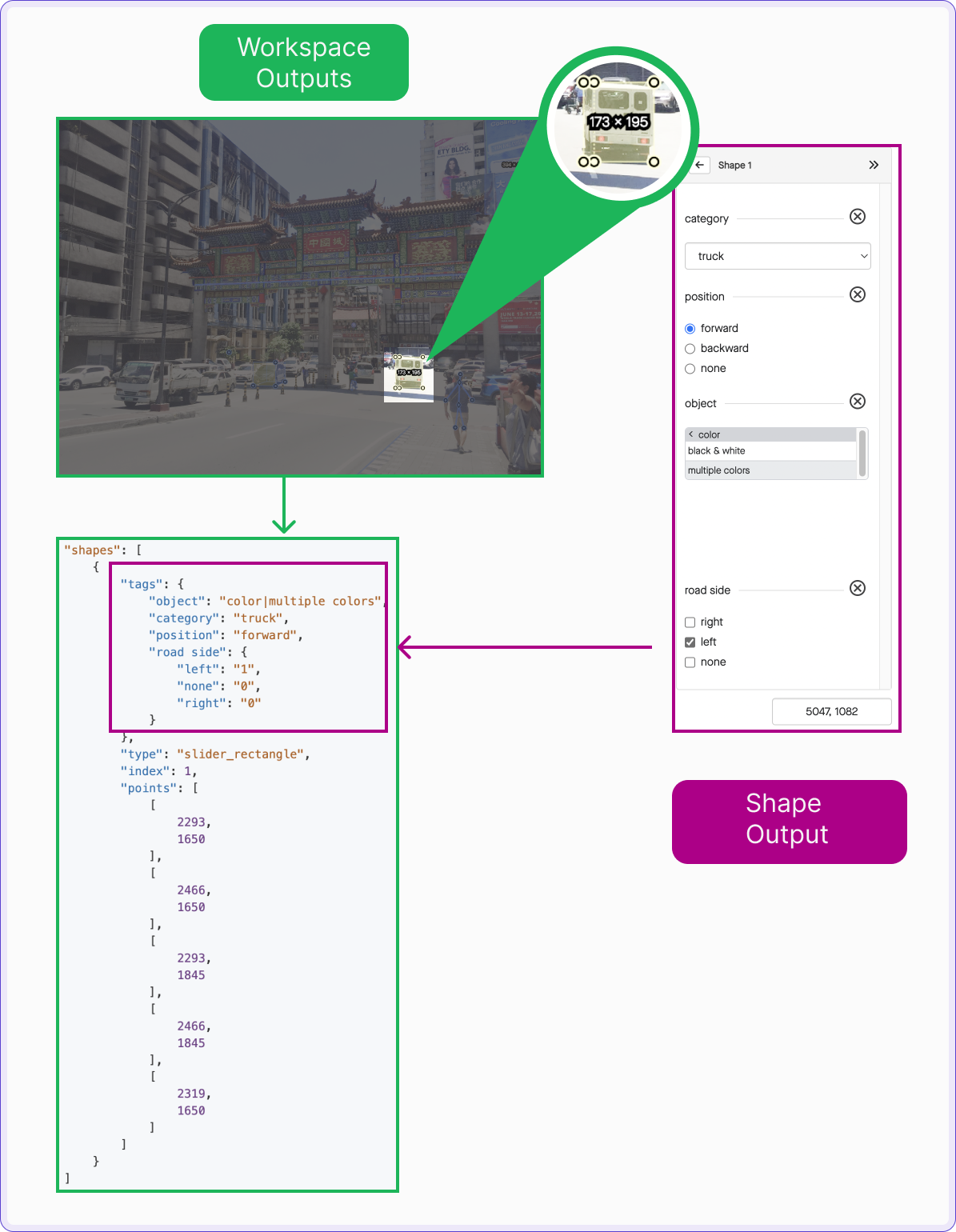
Annotation Output
When working with annotations, it is essential to understand how they are represented in JSON format. While tasks and their annotations are visible in the workspace, the corresponding JSON structure provides a deeper insight into how the data is organized and stored.
In this example, we are going to zoom in on the slider rectangle tool to explore how its output is represented in JSON. It’s worth mentioning that each output type differs in the JSON structure. While some follow similar patterns, others have distinct formats, all of which are thoroughly documented in the accompanying recipe review the section output type.